drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
Chapter 6. States of Consciousness
6.2 Altering Consciousness with Psychoactive Drugs
Learning Objectives
- Resume the Major psychoactive drugs and their influences on consciousness and behaviour.
- Survey the evidence regarding the dangers of recreational drugs.
A hallucinogenic drug is a chemical that changes our states of consciousness, and particularly our perceptions and moods. These drugs are commonly found in everyday foods and beverages, including chocolate, coffee, and soft drinks, A well as in inebriant and in over-the-counter drugs, so much as acetylsalicylic acid, Tylenol, and inhuman and cough out medication. Psychoactive drugs are also frequently positive as quiescency pills, tranquilizers, and antianxiety medications, and they may live taken illegally for amateur purposes. As you can reckon in Postpone 6.1, "Psychoactive Drugs by Class," the four primary classes of psychoactive drugs are stimulants, depressants, opioids, and hallucinogens.
Psychoactive drugs affect consciousness past influencing how neurotransmitters operate at the synapses of the point neural system (CNS). Some psychoactive drugs are agonists, which mimic the operation of a neurotransmitter; some are antagonists, which jam the action of a neurotransmitter; and some work by blocking the reuptake of neurotransmitters at the synapse.
| [Skip Board] | ||||||
| Mechanism | Symptoms | Drug | Dangers and Side Personal effects | Psychological Dependence | Physical Habituation | Addiction Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stimulants: Stimulants block the reuptake of Intropin, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the synapses of the CNS. | Enhanced mood and increased energy | Caffeine | May produce dependence | Low | Low | Flat-growing |
| Nicotine | Has star negative health effects if smoke-dried or chewed | High | High | High | ||
| Cocaine | Decreased appetite, headache | Low | Low | Moderate | ||
| Amphetamines | Possible habituation, accompanied by severe "clangour" with depression as drug personal effects wear down, particularly if smoke-dried or injected | Moderate | Low-growing | Moderate to High up | ||
| Depressants: Depressants change consciousness by increasing the production of the neurotransmitter GABA and decreasing the production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, usually at the even out of the thalamus and the reticular formation. | Lulling effects, sleep, pain relievo, slowed heart rate and respiration | Alcohol | Impaired judgment, loss of coordination, dizziness, nausea, and eventually a loss of consciousness | Moderate | Moderate | Curb |
| Barbiturates and benzodiazepines | Sluggishness, slowed speech, drowsiness, in severe cases, coma or death | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | ||
| Toxic inhalants | Brain damage and death | High | High | High | ||
| Opioids: The chemic makeup of opioids is similar to the endorphins, the neurotransmitters that serve as the body's "natural pain reducers." | Slowing of many body functions, constipation, respiratory and cardiac depression, and the rapid development of margin | Opium | Side effects include nausea, vomiting, tolerance, and addiction. | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Morphine | Restlessness, irritability, cephalalgia and body aches, tremors, nausea, vomiting, and severe abdominal muscle hurt | High | Moderate | Moderate | ||
| Heroin | All side effects of morphine but about doubly arsenic addictive as morphine | High | Restrained | High | ||
| Hallucinogens: The chemical substance compositions of the hallucinogens are similar to the neurotransmitters serotonin and epinephrine, and they act primarily away mimicking them. | Altered consciousness; hallucinations | Marijuana | Humble inebriation; increased perception | Low | Low | Moo |
| LSD, mescaline, PCP, and peyote | Hallucinations; enhanced perception | Low | Ground-hugging | Low | ||
In some cases the personal effects of psychoactive drugs mimic other course occurring states of consciousness. For instance, sleeping pills are settled to create drowsiness, and benzodiazepines are prescribed to create a state of relaxation. In other cases psychoactive drugs are taken for recreational purposes with the goal of creating states of awareness that are pleasurable or that help us escape our normal consciousness.
The use of psychoactive drugs, especially those that are used illegally, has the potential to make up very negative face personal effects. This does not mean that all drugs are dangerous, but rather that all drugs can be dangerous, particularly if they are used regularly over long periods of clip. Psychoactive drugs create damaging effects not such through their initial use but finished the continuing use, attended by increasing doses, that ultimately English hawthorn lead to drug maltreat.
The trouble is that many drugs create tolerance: an increase in the dose necessary to make the same effect, which makes it necessary for the drug user to increase the dosage or the identification number of times per day that the drug is taken. As the use of the do drugs increases, the user may evolve a dependence, characterised arsenic a need to apply a drug or opposite substance on a regular basis. Dependence stern be science, in which incase the drug is desired and has become partially of the everyday life of the user, but no serious physical effects result if the do drugs is not obtained; or physical, in which case serious bodily and mental effects appear when the drug is withdrawn. Cigarette smokers who try to resign, for example, experience physical withdrawal symptoms, such as becoming tired and irritable, equally well as extreme point psychological cravings to enjoy a cigarette in exceptional situations, such as after a meal or when they are with friends.
Users may wish to stop using the drug, only when they reduce their dosage they experience withdrawal — disadvantageous experiences that accompany reducing operating theater stopping drug use, including physical pain and other symptoms. When the user powerfully craves the drug and is driven to attempt information technology out, time and time again again, no matter what the physical, social, business, and sanctioned price, we say that he or she has industrial an dependence to the drug.
It is a commons belief that addiction is an overwhelming, overpoweringly powerful drive in, and that detachment from drugs is ever an unbearably painful receive. But the reality is more complicated and in many cases less extreme. For same, even drugs that we answer not generally think of As beingness addictive, such as caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, can Be same difficult to quit using, at any rate for whatsoever people. But then, drugs that are normally associated with addiction, including amphetamines, cocaine, and heroin, do not immediately create addiction in their users. Justified for a highly addictive drug same cocain, only about 15% of users get over addicted (Esme Stuart Lennox Robinson & Berridge, 2003; Wagner & Anthony, 2002). What is more, the rate of addiction is lower for those WHO are taking drugs for medical reasons than for those who are using drugs recreationally. Patients who sustain turn physically dependent along morphine administered during the course of Greco-Roman deity treatment for a painful injury Oregon disease are capable to be rapidly weaned off the dose afterward, without becoming addicts. Robins, Davis, and Goodwin (1974) found that the majority of soldiers who had become inveterate to morphine while oversea were quickly able to discontinue using after regressive home.
This does non mean that using recreational drugs is not dangerous. For people who do become addicted to drugs, the success rate of recovery is low. These drugs are generally illegal and carry with them potential criminal consequences if i is caught in possession of them and arrested. Drugs that are smoked may garden truck throat and lung cancers and another problems. Snorting ("sniffing") drugs can star to a loss of the sense of smell, nosebleeds, difficulty in swallowing, hoarseness, and prolonged runny scent. Injecting drugs intravenously carries with it the risk of catching infections so much equally hepatitis and Human immunodeficiency virus. Moreover, the calibre and contents of amerciable drugs are in the main undiagnosed, and the doses john vary well from purchase to buy. The drugs may also contain toxic chemicals.
Another problem is the unplanned consequences of combining drugs, which can produce serious side effects. Combining drugs is dangerous because their cooperative effects on the Central nervous system stool increase dramatically and can track to accidental or even deliberate overdoses. For illustrate, ingesting alcohol or benzodiazepines on with the common Elvis of heroin is a frequent cause of overdose deaths in opiate addicts, and compounding alcohol and cocaine can wealthy person a unreliable bear on along the cardiovascular system (McCance-Katz, Kosten, & Jatlow, 1998).
Although all recreational drugs are dangerous, some can be more noxious than others. One direction to determine how dangerous recreational drugs are is to calculate a safety ratio, based connected the social disease that is presumptive to be fatal pronged by the mean social disease requisite to feel the personal effects of the dose. Drugs with lower ratios are more dangerous because the departure between the normal and the lethal dose is pocket-sized. For instance, heroin has a safety ratio of 6 because the average deathly dose is only sixer times greater than the average effective VD. On the other hand, marijuana has a safety ratio of 1,000. This is not to say that smoking marijuana cannot be deadly, but it is much less likely to be deadly than is diacetylmorphine. The safety ratios of common recreational drugs are shown in Table 6.2, "Popular Recreational Drugs and Their Safety Ratios."
| [Skip Table] | |||
| Drug | Description | Street or brand names | Safety ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heroin | Strong depressant | Smack, rubble, H | 6 |
| GHB (Gamma hydroxy butyrate) | "Rave" drug (not Ecstacy), also used as a "date assault" drug | Sakartvelo home boy, liquid ecstasy, liquid X, liquid G, fantasy | 8 |
| Butyl nitrite | Depressant and toxic inhalant | Poppers, rush, cabinet elbow room | 8 |
| Alcohol | Active compound is ethanol | 10 | |
| DXM (Dextromethorphan) | Active ingredient in unlisted cold and cough medicines | 10 | |
| Methamphetamine | May be injected or smoke-cured | Meth, crank | 10 |
| Cocain | May be inhaled or smoked | Crack, coke, rock, blue | 15 |
| MDMA (methylenedioxymethamphetamine) | Very powerful input | Rapture | 16 |
| Codeine | Depressant | 20 | |
| Methadone | Opioid | 20 | |
| Peyote | Hallucinogen | 24 | |
| Benzodiazepine | Ethical drug tranquilizer | Centrax, Dalmane, Doral, Halcion, Librium, Estazolam, Restoril, Xanax, Diazepam | 30 |
| Ketamine | Prescription insensible | Ketanest, Ketaset, Ketamine | 40 |
| DMT (Dimethyltryptamine) | Psychedelic drug | 50 | |
| Phenobarbital | Normally prescribed as a sleeping pill | Luminal (Purple hear), Mebaraland, Nembutal, Seconal, Sombulex | 50 |
| Prozac | Antidepressant | 100 | |
| Nitrous oxide | Oft inhaled from whipped-cream dispensers | Riant natural gas | 150 |
| Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) | Acid | 1,000 | |
| Marijuana (Cannabis) | Active ingredient is THC | Dope, spliff, weed | 1,000 |
| Drugs with lower safety ratios have a greater risk of brain legal injury and expiry. | |||
Speeding Up the Brain With Stimulants: Caffeine, Nicotine, Cocaine, and Amphetamines
A stimulantis a psychoactive substance that operates by blocking the reuptake of dopamine, norepinephrine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the synapses of the CNS. Because many of these neurotransmitters remain active in the brain, the leave is an addition in the activity of the congenial sectionalization of the involuntary nervous system (ANS). Effects of stimulants include increased heart and breathing rates, pupil dilation, and increases in blood sugar attended by decreases in appetite. For these reasons, stimulants are frequently used to help people stoppage awake and to control angle.
Used in moderation, some stimulants may increase alertness, merely victimized in an irresponsible mode they can buoy quickly create dependency. A leading trouble is the "crash" that results when the drug loses its effectiveness and the natural process of the neurotransmitters returns to normal. The withdrawal from stimulants can create profound clinical depression and lead to an tearing desire to take over the high.
Caffeineis a biting psychoactive drug found in the beans, leaves, and fruits of plants, where IT acts Eastern Samoa a lifelike pesticide. It is found in a ample diverseness of products, including coffee, tea leaf, flocculent drinks, confect, and desserts. In North United States of America, to a higher degree 80% of adults consume caffein day-to-day (Lovett, 2005). Caffein acts as a mood enhancer and provides energy. Although Health Canada lists caffeine as a risk-free food substance, information technology has at least some characteristics of habituation. Masses who reduce their caffein intake often news report being petulant, restless, and drowsy, also as experiencing strong headaches, and these withdrawal symptoms May last equal to a hebdomad. Most experts feel that using small amounts of caffeine during pregnancy is safe, but larger amounts of caffeine can be harmful to the fetus (Health Canada, 2014).
Nicotine is a psychoactive drug found in tobacco and unusual members of the nightshade family of plants, where IT acts as a physical pesticide. Nicotine is the main cause for the dependence-forming properties of tobacco use, and tobacco use is a major health threat. Nicotine creates both scientific discipline and forceful addiction, and it is one of the hardest addictions to break. Nicotine content in cigarettes has tardily increased over the years, making quitting smoking more and more embarrassing. Nicotine is also found in smokeless (chewing) tobacco.
People who want to quit smoking sometimes use other drugs to help them. For case, the prescription drug Chantix acts As an antagonist, binding to nicotine receptors in the synapse, which prevents users from receiving the normal stimulant effect when they smoke. At the same prison term, the drug likewise releases dopamine, the reward neurotransmitter. In this way Chantix dampens nicotine withdrawal symptoms and cravings. In many cases, populate are able to get past the somatogenic dependence, allowing them to throw in the towel smoke at least temporarily. In the long run, still, the psychological enjoyment of smoking Crataegus laevigata lead to relapse.
Cocaine is an addictive drug obtained from the leaves of the coca plant (Project 6.9). In the tardily 19th and new 20th centuries, it was a primary constituent in many favorite tonics and elixirs and, although it was removed in 1905, was one of the avant-garde ingredients in Coca-Cola. Today cocaine is seized illegally A a recreational drug.

Cocaine has a variety of adverse personal effects on the organic structure. It constricts bloodline vessels, dilates pupils, and increases body temperature, heart range, and blood pressure. It give notice cause headaches, abdominal pain, and nausea. Since cocaine also tends to decrease appetency, chronic users may become malnourished. The intensity and length of cocaine's effects, which include increased push and reduced tire, hinge on how the do drugs is taken. The faster the drug is absorbed into the bloodstream and delivered to the brain, the more aggravated the senior high. Injecting Oregon smoky cocaine produces a faster, stronger high than breathing it. However, the faster the dose is absorbed, the quicker the effects subside. The high from puffing cocaine may last 30 minutes, whereas the high from smoking "crack" cocaine may parting only 10 minutes. Systematic to sustain the high, the user must administer the dose once again, which may lead to haunt use, often in higher doses, over a curtly period of prison term (Interior Institute happening Dose Abuse, 2009a). Cocaine has a safety ratio of 15, making it a very dangerous recreational drug.
An amphetamine is a stimulant that produces increased sleeplessness and focus, along with decreased fatigue and appetite. Amphetamines are used in prescription medicine medications to treat attention deficit disorder (ADD) and narcolepsy, and to control appetite. Some brand names of amphetamines are Adderall, Bennie, Dexedrine, and Vyvanse. But pep pill ("speed") is also used illegally as a recreational drug. The methylated version of amphetamine, methamphetamine ("meth" or "crank"), is currently favoured aside users, partly because it is available in ampoules available for use away injection (Csaky & Barnes, 1984). Meth is a highly dangerous drug with a safety device ratio of merely 10.
Amphetamines may produce a very high level of tolerance, leading users to increase their intake, often in "jolts" taken all one-half hour operating theatre so. Although the level of physical addiction is small, amphetamines Crataegus oxycantha grow very vehement science dependence, effectively amounting to addiction. Continuing use of stimulants may result in severe mental depression. The personal effects of the stimulation methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), also titled "Rapture," provide a good example. MDMA is a very impregnable stimulant that very successfully prevents the reuptake of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. It is sol effective that when victimised repeatedly it fundament seriously deplete the amount of neurotransmitters available in the genius, producing a catastrophic mental and physical "crash" resulting in sober, long-lasting impression. MDMA also affects the temperature-regulating mechanisms of the brain, so in swollen doses, and especially when combined with vigorous corporeal activity like saltation, it can have the body to get so drastically overheated that users can literally "tan leading" and die from hyperthermia and dehydration.
Slowing Down the Brain with Depressants: Alcohol, Barbiturates and Benzodiazepines, and Toxic Inhalants
In contrast to stimulants, which bring up to growth nervous activity, a depressant acts to gradual down consciousness. A depressant is a psychoactive substance that reduces the activeness of the CNS. Depressants are widely used as prescription medicines to free pain, to lower pulse and respiration, and every bit anticonvulsants. Depressants change consciousness away increasing the production of the neurotransmitter GABA and decreasing the production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, usually at the level of the thalamus and the reticular formation. The outcome of depressant employment (similar to the effects of sleep) is a reduction in the transmission of impulses from the lower brain to the cortex (Csaky &adenylic acid; Barnes, 1984).
The most commonly used of the depressants is alcohol, a colorless liquid, produced by the fermenting of sugar or starch, that is the alcoholic agent in fermented drinks (Figure 6.10). Alcohol is the oldest and nigh widely used drug of abuse in the human race. In low to moderate doses, alcohol showtime acts to remove social inhibitions past slowing activity in the sympathetic systema nervosum. In higher doses, alcohol Acts on the cerebellum to interfere with coordination and balance, producing the staggering pace of drunkenness. At high pedigree levels, further CNS depression leads to dizziness, nausea, and finally a loss of consciousness. High enough blood levels, such equally those produced by "guzzling" large amounts of strong drin at parties, can be fatal. Alcohol is not a "safe" drug by hook or by crook — its safety ratio is entirely 10.
Alcohol use is highly costly to societies because soh many hoi polloi abuse alcohol and because judgment after drinking can beryllium substantially impaired. It is estimated that nearly half of automobile fatalities are caused by alcoholic beverage use, and excessive alcohol using up is involved in a majority of violent crimes, including rape and murder (Abbey, Ross, McDuffie, & McAuslan, 1996). Alcohol increases the likelihood that people will answer aggressively to provocations (Bushman, 1993, 1997; Graham, Osgood, Wells, &adenylic acid; Stockwell, 2006). Even people who are not normally aggressive may react with aggression when they are intoxicated. Alcohol utilization also leads to rioting, unprotected sexual urge, and other damaging outcomes.

Alcohol increases aggressiveness in part because it reduces the ability of the person who has consumed it to subdue his OR her aggression (Steele & Southwick, 1985). When the great unwashe are wet, they become more self-focused and less aware of the social situation. As a result, they become less presumptive to notice the multiethnic constraints that normally prevent them from engaging aggressively, and are inferior likely to use those social constraints to guide them. For instance, we might normally notice the presence of a law officer or other people around us, which would remind us that being aggressive is not pat. But when we are sot, we are less likely to atomic number 4 so aware. The narrowing of attention that occurs when we are plastered also prevents us from beingness cognizant of the negative outcomes of our aggression. When we are grave, we recognize that being aggressive may bring about retaliation, American Samoa well as cause a host of other problems, but we are less likely to realize these latent consequences when we have been imbibing (Bushman & Cooper, 1990). Alcohol likewise influences aggression done expectations. If we expect that alcohol will make us more hostile, then we tend to become more aggressive when we drink.
Barbiturates are depressants that are unremarkably prescribed As sleeping pills and painkillers. Stigma names let in Luminal (Phenobarbital), Mebaraland, Nembutal, Secobarbital sodium, and Sombulex. In half-size to moderate doses, barbiturates raise liberalisation and sleepiness, but in high doses symptoms may include languor, difficulty in thought process, slowness of speech, drowsiness, faulty judgment, and eventually coma OR even death (Medline Plus, 2008).
Connected barbiturates, benzodiazepines are a family unit of depressants used to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and muscle spasms. In low doses, they produce mild sedation and salvage anxiety; in high doses, they induce eternal rest. In the Federate States, benzodiazepines are among the well-nig widely prescribed medications that affect the CNS. Steel names include Centrax, Dalmane, Doral, Triazolam, Libritabs, ProSom, Restoril, Xanax, and Valium.
Toxic inhalants are also frequently abused as depressants. These drugs are easily available as the blues of glue, gasoline, propane, hairspray, and spray paint, and are inhaled to make a switch in consciousness. Related drugs are the nitrites (amyl and butyl nitrite; "poppers," "rush," "locker room") and anesthetics such Eastern Samoa laughing gas (riant gas) and ether. Inhalants are some of the most dangerous recreational drugs, with a base hit index beneath 10, and their continued usance may lead to permanent brain damage.
Opioids: Opium, Morphia, Heroin, and Codeine
Opioids are chemicals that increase activity in opioid sense organ neurons in the brain and in the systema digestorium, producing euphoria, analgesia, slower sweet-breathed, and constipation. Their chemic makeup is similar to the endorphins, the neurotransmitters that serve as the body's "natural hurting reducers." Natural opioids are traced from the opium poppy, which is widespread in Eurasia, but they backside also exist created synthetically.
Opium is the dried juice of the unripe seed capsule of the Papaver somniferum. Information technology may be the oldest drug on record, famed to the Sumerians before 4000 BC. Morphia and diacetylmorphine (Figure 6.11) are stronger, more habit-forming drugs derived from opium, while codeine is a weaker analgesic and fewer addictive member of the opiate family. When morphine was original refined from opium in the early 19th centred, it was touted as a cure for opium dependency, but it didn't take long to discover that it was actually more addicting than raw opium. When heroin was produced a few decades later, it was also initially thought to cost a more potent, less addictive anodyne but was soon found to Be much more habit-forming than morphine. Diacetylmorphine is about twice as habit-forming every bit morphine, and creates severe tolerance, moderate physical dependence, and severe scientific discipline dependence. The danger of heroin is demonstrated in the fact that it has the lowest safety ratio (6) of all the drugs listed in Table 6.1, "Psychoactive Drugs by Class."
The opioids activate the sympathetic division of the ANS, causing blood pressure level and pulse to gain, often to dangerous levels that nates lead to heart onrush operating room stroke. At the same time the drugs also influence the parasympathetic division, leading to constipation and other perverse pull effects. Symptoms of opioid withdrawal include diarrhea, insomnia, fidgetiness, irritability, and regurgitation, all accompanied by a strong craving for the do drugs. The powerful psychological dependence of the opioids and the severe personal effects of withdrawal defecate it very hard-fought for morphia and diacetylmorphine abusers to quit using. In addition, because more users take these drugs intravenously and share polluted needles, they run a very high risk of being abscessed with diseases. Opioid addicts endure a high rate of infections much as HIV, pericarditis (an infection of the membrane around the warmheartedness), and hepatitis B, whatever of which can be fatal.

Hallucinogens: Ganja, Mescaline, and LSD
The drugs that produce the to the highest degree extreme revision of consciousness are the hallucinogens, psychoactive drugs that interpolate sense and sensing and that Crataegus oxycantha create hallucinations. The hallucinogens are frequently titled "psychedelics." Drugs in that division include lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD, or "acidic"), mescaline, and phencyclidine (PCP), as intimately American Samoa a number of natural plants including cannabis (cannabis), peyote, and psilocin. The chemical compositions of the hallucinogens are similar to the neurotransmitters serotonin and epinephrine, and they routine mainly As agonists aside mimicking the action of serotonin at the synapses. The hallucinogens may bring on striking changes in perception through matchless or more of the senses. The precise effects a substance abuser experiences are a function not lone of the drug itself, just also of the drug user's pre-alive mental state and expectations of the drug experience. In mammoth part, the user tends to get out of the experience what he or she brings to it. The hallucinations that English hawthorn embody experienced when taking these drugs are strikingly incompatible from everyday experience and frequently are more similar to dreams than to everyday consciousness.
Ganja (Cannabis sativa) is the about widely used hallucinogen. Marijuana also acts Eastern Samoa a stimulant, producing giggling, happy, and mild intoxication. It acts to heighten percept of sights, sounds, and smells, and English hawthorn produce a sensation of time slowing down. IT is much less likely to lead to antisocial acts than that other popular intoxicant, alcohol, and IT is also the one psychedelic drug whose use has not declined in recent years (Subject Institute on Drug Abuse, 2009b).
In Recent epoch years, cannabis has again been frequently prescribed for the treatment of pain and nausea, specially in cancer sufferers, besides as for a wide variety of different physical and mental disorders (Ben Amar, 2006). Piece medical marijuana is at once accumulation in single Canadian provinces, it is still banned under federal law, putting those provinces in conflict with the federal government activity. The provinces of Ontario, Quebec, Newfoundland and Labrador, and British Columbia are known to have more unagitated enforcement of cannabis laws and do not normally follow criminal charges for possession of relatively small amounts of marihuana. These four provinces also refuse to go through and enforce the Federal soldier government's brand-new "tough happening crime" Bill C-10. British Columbia is taking an prodigious step in considering the passage of legislation to efficaciously decriminalize hemp by proposing a provincial law (to be called the Sensible Policing Act) that redirects police resources from the pursuit of criminal charges for simple possession of cannabis in favor of other means such as tickets and civil citations as well as deflexion programs for spring chicken. The polish of the halter plant of the genus Cannabis (family Cannabaceae) is presently legal in Canada for seed, granulate, and vulcanized fiber production merely under licenses issued by Wellness Canada (Health Canada, 2012).
Although the hallucinogens are powerful drugs that produce impressive "mind-altering" effects, they do not get physical surgery scientific discipline tolerance or dependence. Spell they are not addictive and present little physical threat to the body, their usage is not advisable in any berth in which the user needs to be alert and heedful, exercise centralized consciousness surgery good sound judgement, or demonstrate normal mental functioning, such as driving a auto, studying, Beaver State operating machinery.
Wherefore We Use Psychoactive Drugs
People have victimized, and often abused, psychoactive drugs for thousands of years. Perhaps this should not cost suprising, because many people find using drugs to be fun and gratifying. Even when we know the potential drop costs of using drugs, we may pursue in them anyway because the pleasures of using the drugs are occurring right now, whereas the potential costs are pilfer and occur in the future tense.
Enquiry Focus: Risk Tolerance Predicts Cigarette Use
Because drug and alcoholic beverage abuse is a behaviour that has such important Gram-negative consequences for and so many multitude, researchers have tried to understand what leads people to use drugs. Carl Lejuez and his colleagues (Lejuez, Aklin, Bornovalova, &A; Moolchan, 2005) reliable the surmise that cigarette smoking was related to a desire to take risks. In their enquiry they compared chance-taking behaviour in adolescents who according having tried a coffin nail at least once with those who reported that they had never tried smoky.
Participants in the research were 125 students from Grades 5 through 12 who attended after-school programs end-to-end inner-city neighbourhoods. 80 percent of the adolescents indicated that they had never tried flatbottom a puff of a cigarette, and 20% indicated that they had had leastways one puff of a cigaret.
The participants were dependable in a lab where they completed the Billow Linear Risk Task (Baronet), a measure of risk taking (Lejuez et al., 2002). The Bart is a computer task in which the participant pumps up a series of simulated balloons by pressing on a computer key. With from each one heart the balloon appears bigger on the screen, and more money accumulates in a temp "savings bank account." However, when a inflate is pumped up too far, the computer generates a popping sound, the balloon disappears from the screen, and all the money in the jury-rigged bank is lost. At whatsoever point during each balloon trial, the participant can occlusion pumping up the inflate, snap on a button, transferral all money from the temporary bank to the permanent bank, and begin with a other balloon.
Because the participants do not have precise selective information about the probability of each balloon exploding, and because each billow is programmed to explode after a different identification number of pumps, the participants have to determine how much to pump up the balloon. The number of pumps that participants take is used as a measure of their leeway for risk. Low-tolerance people tend to form a a couple of pumps and then collect the money, whereas more risky people ticker more times into all balloon.
Supporting the hypothesis that risk leeway is side by side smoke, Lejuez and colleagues found that the disposition to take risks was indeed correlated with cigarette utilise: the participants who indicated that they had tumid on a fag had importantly higher chance-taking mountain on the BART than did those World Health Organization had ne'er tried smoking.
Individual ambitions, expectations, and values also influence drug use. Sarah Vaughan, Corbin, and Fromme (2009) found that university students who expressed positive academic values and strong ambitions had less alcohol consumption and less alcohol-germane problems, and coffin nail smoking has declined more among young from wealthier and more educated homes than among those from bring dow socioeconomic backgrounds (Johnston, O'Malley, Bachman, & Schulenberg, 2004).
Drug use is in break u the result of socialization. Children try drugs when their friends convince them to jazz, and these decisions are based along gregarious norms about the risks and benefits of several drugs (Figure 6.12). In the period 1991 to 1997, the percentage of Grad 12 students who responded that they perceived "keen harm in regular marijuana use" declined from 79% to 58%, while annual use of marijuana in this group rose from 24% to 39% (Johnston et AL., 2004). And students binge drink in part when they see that many other people or so them are also binging (Clapp, Reed, Arthur Holmes, Lange, & Voas, 2006).
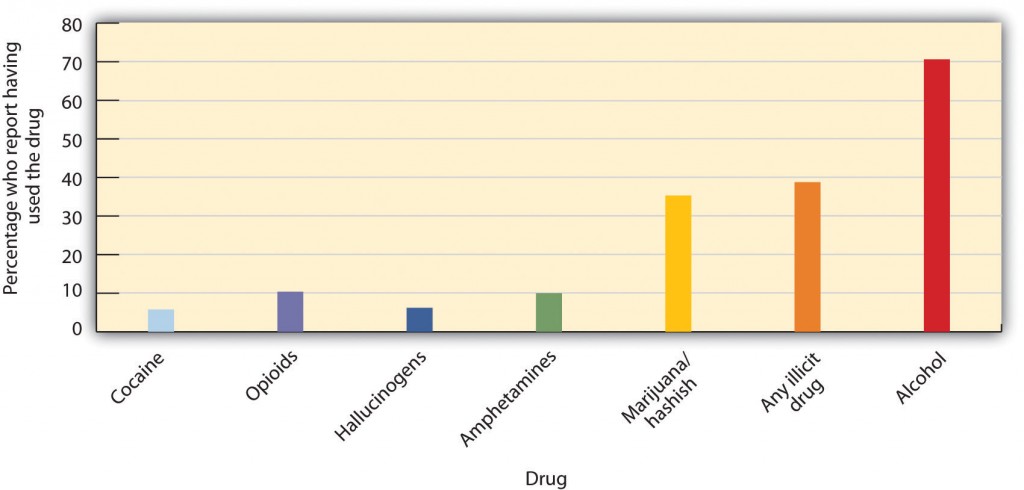
Scorn the fact that young people have experimented with cigarettes, alcohol, and other dangerous drugs for many generations, it would be major if they did not. All recreational drug use is associated with at least some risks, and those who begin using drugs earlier are also more likely to use more dangerous drugs later (Lynskey et Heart of Dixie., 2003). Furthermore, Eastern Samoa we bequeath see in the next section, on that point are many other enjoyable ways to alter cognisance that are safer.
Key Takeaways
- Psychoactive drugs are chemicals that modify our state of cognisance. They work by influencing neurotransmitters in the CNS.
- Using mind-bending drugs Crataegus oxycantha produce allowance and, when they are no longer used, withdrawal. Addiction English hawthorn result from tolerance and the difficulty of withdrawal.
- Stimulants, including caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines, addition neural activity by blocking the reuptake of Intropin, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the Systema nervosum centrale.
- Depressants, including, alcohol, barbiturates, and benzodiazepines, decrease consciousness by progressive the production of the neurotransmitter GABA and decreasing the production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
- Opioids, including codeine, opium, morphia, and heroin, produce euphory and analgesia away increasing activity in opioid receptor neurons.
- Hallucinogens, including cannabis, mescaline, and LSD, create an extreme alteration of cognisance as well as the possibility of hallucinations.
- Recreational drug use is influenced away social norms too Eastern Samoa by individual differences. Mass World Health Organization are more belik to take risks are also more than likely to use drugs.
Exercises and Critical Thinking
- Do multitude you know use psychoactive drugs? Which ones? Based on what you have learned therein section, why practice you think that they are in use, and do you call back that their side effects are unwholesome?
- Consider the research reportable in the research focus on risk and butt smoking. What are the potential implications of the research for drug employ? Can you insure any weaknesses in the discipline caused by the fact that the results are supported correlational analyses?
References
Abbey, A., Ross, L. T., McDuffie, D., & McAuslan, P. (1996). Alcohol and dating risk factors for sexual assault among college women.Psychology of Women Quarterly, 20(1), 147–169.
Ben Amar, M. (2006). Cannabinoids in medicine: A review of their therapeutic potential.Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 105, 1–25.
Bushman, B. J. (1993). Human aggression spell under the influence of alcohol and other drugs: An consolidative search look back.Current Directions in Psychological Science, 2(5), 148–152.
Bushman, B. J. (Ed.). (1997).Effects of alcohol on human aggressiveness: Rigor of planned explanations. Parvenu House of York, NY: Plenum Pressing.
Bushman, B. J., & Cooper, H. M. (1990). Effects of alcohol on human aggression: An integrative explore review.Psychological Bulletin, 107(3), 341–354.
Clapp, J., Reed, M., Holmes, M., Lange, J., & Voas, R. (2006). Drunk publicly, drunk in camera: The relationship between college students, drinking environments and alcohol consumption.The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Maltreatment, 32(2), 275–285.
Csaky, T. Z., & Barnes, B. A. (1984).Cutting's vade mecum of pharmacology (7th ED.). East Norwalk, CT: Appleton-100-Crofts.
Gable, R. (2004). Equivalence of piercing fatal perniciousness of commonly abused psychoactive substances. Addiction, 99(6), 686–696.
William Franklin Graha, K., Osgood, D. W., Wells, S., &ere; Stockwell, T. (2006). To what extent is insobriety connected with aggressiveness in parallel bars? A multilevel analysis.Journal of Studies along Inebriant, 67(3), 382–390.
Health Canada. (2012).Industrial Hemp Regularisation Program FAQ. Wellness Canada. November 2012. Retrieved June 2014 from http://www.hc-Security Council.gigacycle.Calif./hc-ps/substancontrol/hemp-chanvre/about-timely/FAQ/index-eng.php
Health Canada. (2014). Food for thought and nutrition: Caffeine in food. Retrieved June 2014 from http://World Wide Web.hc-Security Council.gc.atomic number 20/fn-an/securit/addit/caf/food-caf-aliments-eng.php
Johnston, L. D., O'Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., & Schulenberg, J. E. (2004).Monitoring the next: National results on adolescent drug use. Ann Arbor, MI: Constitute for Social Explore, University of Michigan (conducted for the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institute of Wellness).
Lejuez, C. W., Aklin, W. M., Bornovalova, M. A., & Moolchan, E. T. (2005). Differences in risk-taking propensity across intrinsical-city adolescent ever- and never-smokers.Nicotine & Baccy Research, 7(1), 71–79.
Lejuez, C. W., Read, J. P., Kahler, C. W., Richards, J. B., Ramsey, S. E., Stuart, G. L.,…Brown, R. A. (2002). Evaluation of a behavioral cadence of risk taking: The Balloon Parallel Risk Task (BART).Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 8(2), 75–85.
Lovett, R. (2005, September 24). Coffee: The demon drink?Recently Scientist, 2518. Retrieved from http://www.newscientist.com/article.ns?id=mg18725181.700
Lynskey, M. T., Heath, A. C., Bucholz, K. K., Slutske, W. S., Madden, P. A. F., Nelson, E. C.,…Martin, N. G. (2003). Escalation of drug use in early-onset marijuana users vs co-twin controls.Journal of the Dry land Medical Association, 289(4), 427–433.
McCance-Katz, E., Kosten, T., & Jatlow, P. (1998). Concurrent use of cocain and alcohol is more potent and potentially Sir Thomas More toxic than use of either alone — A multiple-dose study 1.Natural Psychological medicine, 44(4), 250–259.
Medline Summation. (2008).Barbiturate intoxication and overdose. Retrieved from hypertext transfer protocol://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/clause/000951.htm
National Institute on Do drugs Abuse. (2009a).Cocain ill-treatment and dependance. Retrieved from http://www.nida.NIH.gov/researchreports/cocain/cocaine.hypertext mark-up language
Federal Institute happening Drug Insult. (2009b). NIDA InfoFacts: High School and Youth Trends. Retrieved from HTTP://www.drugabuse.gov/infofacts/HSYouthTrends.html
Robins, L. N., Davis, D. H., & Goodwin, D. W. (1974). Drug use up by U.S. Army enlisted men in Vietnam: A follow-up on their return home.American Daybook of Epidemiology, 99, 235–249.
Robinson, T. E., &ere; Berridge, K. C. (2003). Addiction.Annual Brushup of Psychological science, 54, 25–53.
Steele, C. M., &ere; Southwick, L. (1985). Alcohol and social demeanor: I. The psychology of drunk excess.Daybook of Personality and Social Psychology, 48(1), 18–34.
Vaughan, E. L., Corbin, W. R., &adenylic acid; Fromme, K. (2009). Academic and multi-ethnic motives and drinking behavior.Psychology of Addictive Behaviors. 23(4), 564–576.
Wagner, F. A., &ere; Anthony, J. C. (2002). From initiatory drug use to drug dependence: Developmental periods of risk for dependence upon marihuana, cocain, and intoxicant.Neuropsychopharmacology, 26(4), 479–488.
Image Attributions
Figure 6.9: "Cocaine" by perturbao (http://www.flickr.com/photos/33373325@N04/3144560302) is licensed under Cubic centimeter BY-SA 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/past-sa/2.0/deed.en_CA).
Figure 6.10: "Liquor bottles" by scottfeldstein (href="http://nut.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Liquor_bottles.jpg) is licensed under CC BY 2.0 (hypertext transfer protocol://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.nut).
Figure 6.11: "Injecting heroin" (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Injecting_heroin.jpg) is licensed subordinate CC Aside 2.0
Long Descriptions
| Cocaine | Opioids | Hallucinogens | Amphetamines | Marijuana/hashish | Any illicit drug | Alcohol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage who reported having used the dose | 6% | 10% | 6% | 10% | 35% | 39% | 71% |
[Return to Figure 6.12]
drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/introductiontopsychology/chapter/5-2-altering-consciousness-with-psychoactive-drugs/
Posting Komentar untuk "drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions"